The Role of Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cuts in Economic Shaping
Understanding Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cuts
Definition and Purpose of Interest Rate Cuts
The Federal Reserve (Fed) manages the nation's monetary policy. It aims to maintain price stability, promote maximum sustainable employment, and provide moderate, long-term interest rates. A rate cut is when the Fed lowers the target for the federal funds rate.
This is the rate at which banks lend to each other overnight. The primary purpose is to stimulate economic activity by reducing borrowing costs.
Mechanism of Action: How Rate Cuts Influence the Economy
Lowering interest rates makes borrowing cheaper for consumers and businesses. This encourages spending, investment, and economic growth. It can also influence inflation, asset prices, and exchange rates.
The Fed has several tools to enact monetary policy. These include open market operations, the discount rate, reserve requirements, and interest on reserve balances.

Current Economic Landscape: Impact of Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cuts
Analysis of the Recent Rate Cuts and Their Immediate Effects
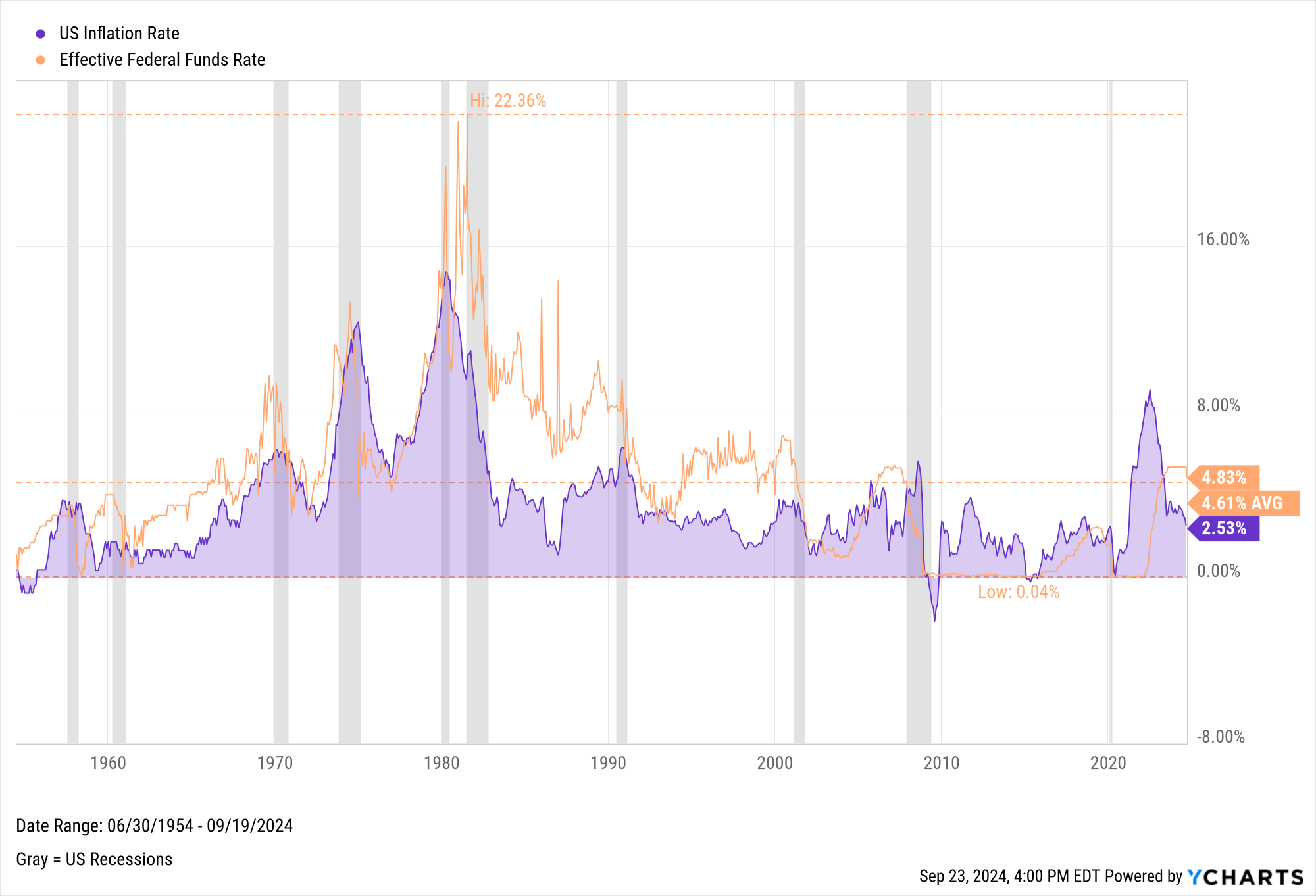
The Federal Reserve implemented its third consecutive rate cut of 2024 on December 18. The Fed reduced its benchmark federal funds rate by 25 basis points to a range of 4.25% to 4.50%. This followed earlier cuts in September (50 basis points) and November (25 basis points).
The immediate effects included a slight dip in equity markets. However, markets rebounded the following day, reflecting a recalibration of investor expectations.
Long-term Economic Implications of Federal Reserve Rate Adjustments
The long-term implications of these rate adjustments are multifaceted. Lower rates can stimulate economic growth, but they also pose risks. These risks include inflation and asset bubbles if not managed carefully.
The Fed's decisions are influenced by various economic indicators. These include GDP growth, inflation rates, and employment figures.
Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cuts and Inflation Trends
Relationship Between Rate Cuts and Inflation Rates
Rate cuts can lead to increased inflation if the economy is already operating near full capacity. Lower borrowing costs can drive up demand, potentially outpacing supply and pushing prices higher. The Fed aims to balance stimulating growth with keeping inflation in check.
The relationship between interest rates and inflation is direct. This means that rates rise in order to keep inflation in check.
Historical Trends: How Rate Cuts Have Affected Inflation in the Past
Historically, rate cuts have been used to combat economic downturns. However, prolonged periods of low rates can lead to inflationary pressures. The Fed monitors inflation closely, using tools like the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index.
For example, the Core PCE, the Fed's preferred inflation gauge, has eased from over 5.5% in 2022 to 2.6% in June 2024. This shows the impact of policy tightening from a near-zero federal funds rate in early 2022.
Predictions for Future Federal Reserve Interest Rate Changes
Current Economic Indicators Influencing Future Rate Decisions
Key economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment rates, and inflation figures play a crucial role. The Fed also considers global economic conditions and financial market stability. Consumer spending remains solid, driven primarily by wealthier cohorts.
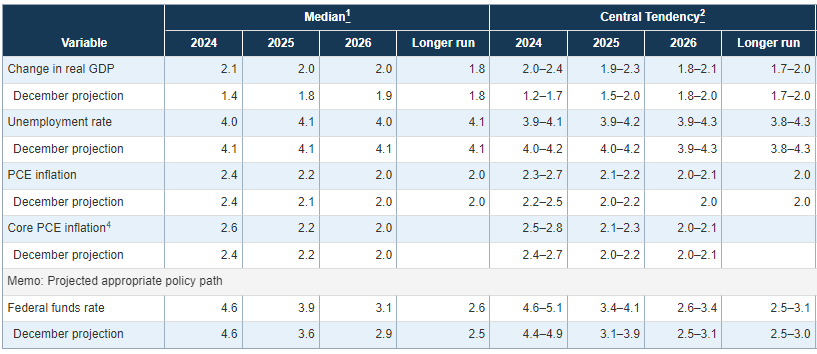
In 2024, the Fed increased its GDP growth forecast to 2.5%. This indicates a stronger economy than anticipated.
Expert Opinions on Future Rate Cut Projections
Experts predict that the Fed will continue to adjust rates based on incoming data. The Summary of Economic Projections (SEP) suggests two 25 basis point cuts in 2025. This is down from four projected in September.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell emphasized the need for caution. He stated, "We still see ourselves on track to cut, but it will depend on the data."
Impact of Rate Cuts on Mortgage Rates and Loans
Direct Effects of Federal Reserve Cuts on Mortgage Rates
While the Fed doesn't directly set mortgage rates, its decisions influence them. Rate cuts generally lead to lower mortgage rates, making home buying more affordable. However, the relationship isn't always direct or immediate.
Mortgage rates are also influenced by factors like the 10-year Treasury yield. They are also influenced by the supply and demand dynamics in the housing market.
Broader Implications for Borrowers and the Housing Market
For borrowers, lower mortgage rates can mean significant savings over the life of a loan. This can stimulate demand in the housing market, potentially leading to increased home sales and construction activity. However, it's essential to consider other factors.
These include housing inventory levels and overall economic conditions. You can learn more about these trends in our post on What Are The Latest Trends In Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cuts?.
Conclusion: The Broader Economic Implications of Rate Cuts
Summary of Key Insights
Federal Reserve rate cuts are a powerful tool for influencing the economy. They can stimulate growth, but also pose risks like inflation. The Fed's recent actions reflect a cautious approach.
They are balancing the need to support economic activity with managing inflation. The long-term impact will depend on various factors.
Final Thoughts on the Future Economic Landscape
The future economic landscape will be shaped by how effectively the Fed manages monetary policy. As economic data evolves, the Fed will adjust its approach. They will aim to maintain a stable and prosperous economy.
Investors and consumers should stay informed about these developments. Understanding the implications of rate cuts can help in making sound financial decisions.
Key Takeaways:
- Rate cuts aim to stimulate economic activity by lowering borrowing costs.
- Recent cuts have immediate and long-term effects on markets and the economy.
- Inflation management is crucial when implementing rate cuts.
- Future rate decisions depend on economic indicators and expert insights.
- Mortgage rates are influenced by Fed decisions, impacting borrowers and the housing market.
