Latest Trends in Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cuts
Overview of Recent Federal Reserve Actions
The Federal Reserve (Fed) has made multiple rate cuts recently. They lowered the target interest rate range to 4.25% to 4.50% in December 2024. This was a 25-basis point reduction.
This change shows the Fed's commitment to maximum employment and price stability. The Fed signaled a slower pace of rate cuts in 2025.
Key Factors Influencing Current Rate Cuts
Economic Indicators Impacting Rate Decisions
Several economic indicators influence the Fed's decisions. Inflation remains a key concern, though it is below post-pandemic highs. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) climbed 2.7% in November, above the 2.6% seen the previous month.
Retail sales also climbed, suggesting a strong economy. Job growth in key sectors like manufacturing has slowed. Hiring rates have plummeted, and job openings continue to fall.
Federal Reserve's Dual Mandate: Inflation vs. Employment
The Fed has a dual mandate: maintaining price stability and maximum employment. They aim for a 2% annual inflation target. Currently, inflation is above this target but far lower than peak levels.

The job market has cooled, with unemployment rising slightly. The Fed must balance controlling inflation with supporting employment. This balance is crucial for economic stability.
Future Projections for Federal Reserve Interest Rates
Expected Rate Cuts in 2024 and 2025
The Fed is expected to continue cutting rates but at a slower pace. In 2024, multiple cuts were made, totaling a 1% reduction since September. For 2025, only two 25-basis point cuts are projected.
J.P. Morgan Research expects the Fed to cut rates by another 25 basis points in December 2024. Further cuts will likely take place once per quarter in 2025. The policy rate is expected to reach 3.5% by the end of the cutting cycle.
Implications of Political Changes on Interest Rate Forecast
Political changes, especially with the incoming Trump administration, add uncertainty. President-elect Trump's proposals on trade, taxation, and immigration could impact inflation. His policies on immigration and trade are particularly significant.
Ending Biden-era asylum programs could affect employment growth. Higher tariffs on China could raise the price level by over 1%. The Fed is monitoring these developments but has not yet incorporated them into their decisions.
Impact of Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cuts on Mortgage Rates
How Rate Cuts Affect Mortgage Borrowing Costs
Rate cuts generally lower borrowing costs, but the impact on mortgage rates is complex. While the Fed's actions influence mortgage rates, they are not the sole determinant. Other factors like the 10-year Treasury yield also play a role.

Lenders often anticipate Fed decisions and adjust rates in advance. This means that by the time a rate cut is announced, many lenders have already factored it in. A modest rate cut may not lead to a significant drop in mortgage rates.
Long-term Trends in Mortgage Rates Post-Cuts
Mortgage rates may not fall dramatically despite rate cuts. Wells Fargo projects that mortgage rates might only fall to around 6.3% in 2025. Fannie Mae also expects rates to stay above 6%.
These rates are lower than the current 7% but higher than the average outstanding mortgage rate of 4%. Homebuyers may still face higher rates compared to previous years. Refinancing opportunities may be slim.
Historical Context of Federal Reserve Interest Rate Changes
Analyzing Historical Rate Trends
The Federal Reserve's interest rate history shows significant fluctuations. In the 1980s, the fed funds rate reached a peak of 19-20% to combat high inflation. Rates have been as low as 0-0.25% during the 2008 financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic.
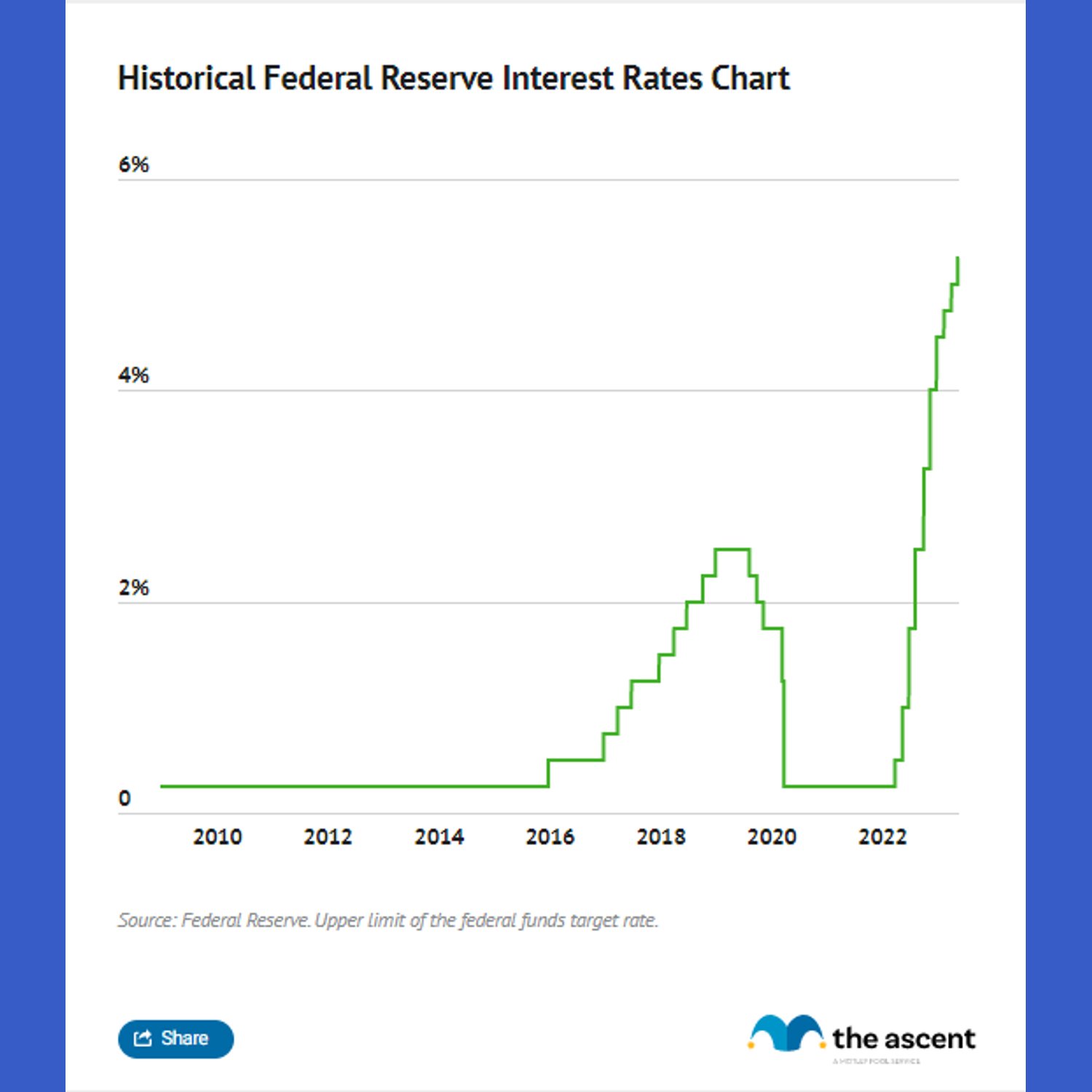
The recent rate hikes were rapid, with 11 increases in about a year and a half. This brought the rate to a 23-year high of 5.25-5.5%. Historical data helps understand the current context and potential future trends.
Lessons from Past Rate Adjustments and Their Economic Impact
Past rate adjustments offer valuable lessons. The Volcker era in the 1980s showed that aggressive rate hikes could tame inflation but at the cost of a recession. The 2008 financial crisis led to near-zero rates and quantitative easing.
These historical events guide the Fed's current actions. The Fed aims to avoid past mistakes by carefully balancing inflation control and economic growth. They strive for a "soft landing" where inflation is controlled without causing a recession.
Conclusion and Future Outlook for Federal Reserve Policies
The Federal Reserve continues to navigate complex economic conditions. The recent rate cuts reflect efforts to balance inflation and employment. Future rate adjustments will depend on economic data and political developments.
The Fed aims to maintain price stability while supporting economic growth. "If the economy evolves broadly as expected, it will likely be appropriate to begin dialing back policy restraint at some point this year," said Jerome Powell in a March congressional testimony. The Fed's decisions will significantly impact borrowing costs and the overall economy.
Key Takeaways:
- The Fed reduced rates to 4.25%-4.50% in December 2024, signaling a slower pace of cuts for 2025.
- Economic indicators like inflation, retail sales, and job growth heavily influence the Fed's decisions.
- Political changes, particularly Trump's policies, add uncertainty to future rate forecasts.
- Mortgage rates are influenced by Fed actions but also by other factors like the 10-year Treasury yield.
- Historical rate trends provide context for current actions, highlighting the Fed's goal of a "soft landing."
Understanding these trends helps consumers and businesses make informed financial decisions. It's crucial to stay updated on economic news and Fed announcements. You may consider reading about how the Bank of Canada's interest rate decisions are shaping your financial future.
